All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
The Surprising Benefits Of Double Glazing In The Summer ... in Salter Point Perth
That window can transfer more solar heat in winter than in summer season. A west-facing window on a summer's afternoon has an angle of occurrence from near 0 approximately 30 with a large efficient location of solar radiation. A north-facing window, in summertime, has a high angle of incidence and a low efficient location of solar radiation, so can transfer less heat than a west-facing one.

You can rapidly and quickly enhance the thermal efficiency of your home by replacing your windows. There are thousands of types of glass and frames to choose from.
Single Vs Double Vs Triple - Which Window Is Right For Your ... in Lynwood WA
There are various types of glass items to pick from. Single glazing uses a single pane of glass. Single glazing with clear glass is not really effective when it pertains to heat loss or gain. To enhance efficiency, you can use single glazing with a more energy-efficient type of glass such as low emissivity (low-e) glass.
Numerous layers can be put together with sealed cavities in between each sheet of glass. IGUs typically use better energy efficiency than single glazing, since they transmit less energy. Nevertheless, the energy efficiency of IGUs also depends upon: the residential or commercial properties of each layer of glass. Various glass types (for instance, clear and low-e glass) can be assembled in an IGU.
Energy Efficient Windows: Choose The Best Option For Your ... in Brentwood WA
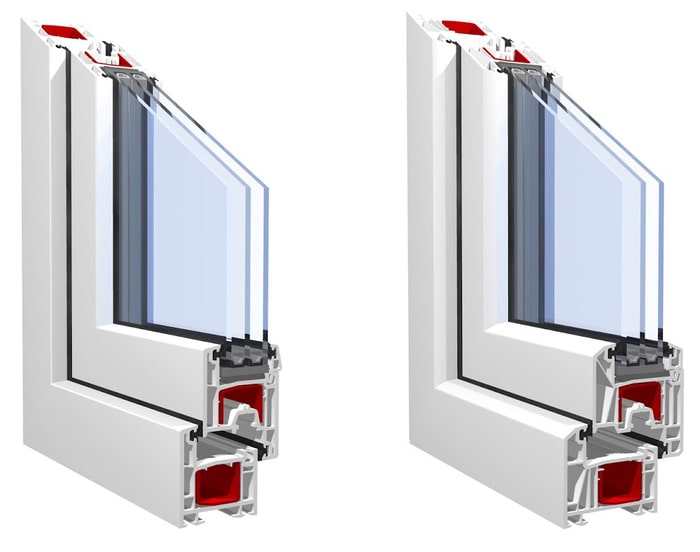
IGU cavities can be filled with air or a more inert, low-conductivity gas such as argon the width of the cavity. Cavity density is normally 6 to 18mm. Wider cavities provide lower (better) U worths, with 12mm usually accepted as the preferred space how well the cavity is sealed. Cavities should be dry and well sealed to avoid moisture getting in.
If argon is installed to the cavity in place of air, moisture is dependably left out the level of desiccant (drying agent). The spacer (metal or polymer strip) that separates the glass layers consists of a desiccant to take in any moisture. Insufficient desiccant might trigger wetness to condense on the glass surface area in cold conditions, minimizing thermal efficiency.
Glazing in Highgate Perth
In reality, IGUs can provide better energy performance for all climates, particularly in heated and air-conditioned houses. Cross-section detail of single, double and triple-glazing systems Low emissivity glass (typically understood as low-e glass) lowers heat transfer. Low-e glass may be either high or low transmission: High transmission low-e glass has a covering that allows daytime from the sun to enter your home to achieve great solar heat gain, but lowers the quantity of the long wavelength infrared heat that can leave back through the window.
Low-e glass has either a pyrolytic coating or a vacuum-deposited thin film metal coating. Pyrolytic finishes are resilient and can be utilized for any glazing; vacuum-deposited coatings are soft and are just utilized within IGUs. Low-e finishings can substantially improve both U worth and SHGC; nevertheless, they should be used properly or they will either deteriorate or stop working to perform as required.
Which Is The Best Type Of Double Glazing? - Which? - Which.co.uk in Lynwood Perth
Low-e coatings can be utilized in combination with clear, toned or reflective glass. Low-e finishings on glazing can lower heat transfer where required Photo: Department of Market, Science, Energy and Resources Toned glass has colouring ingredients consisted of during manufacture. It is available in different colours, generally bronze, grey, blue and green.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Types Of Glazing For Your Windows, Explained in Wembley Downs WA
Single Vs Double Vs Triple - Which Window Is Right For Your ... in Eden Hill WA
Why Install Stunning Double Glazing Windows During Summer? in South Guildford WA
More
Latest Posts
Types Of Glazing For Your Windows, Explained in Wembley Downs WA
Single Vs Double Vs Triple - Which Window Is Right For Your ... in Eden Hill WA
Why Install Stunning Double Glazing Windows During Summer? in South Guildford WA